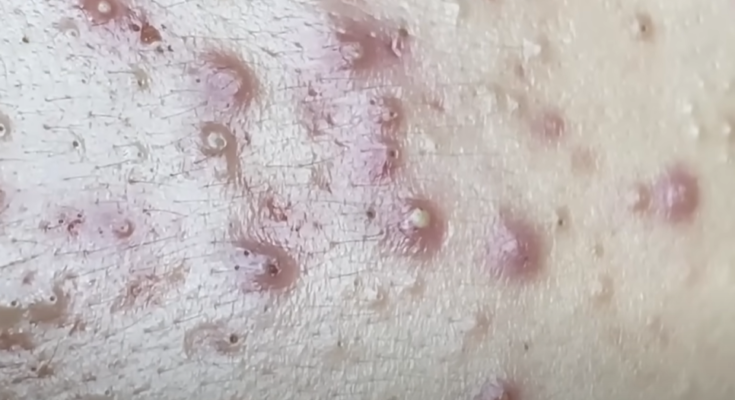
Acne on the face is a common skin condition caused by a combination of factors. The primary cause is the clogging of hair follicles with oil (sebum) and dead skin cells. This creates an environment where bacteria, particularly Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes), can thrive, leading to inflammation and the development of acne lesions.
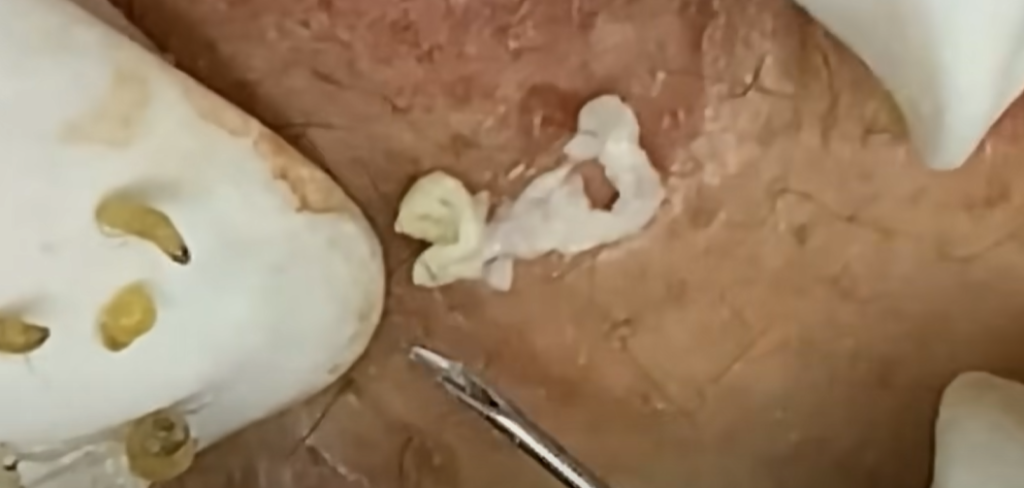
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, especially during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or stress, can increase sebum production. This is why teenagers and women experiencing hormonal shifts are particularly prone to acne.
Excess Oil Production: Overactive sebaceous glands produce more oil, which mixes with dead skin cells and clogs pores.
Poor Skincare Practices: Using comedogenic or unsuitable products, improper cleansing, or excessive scrubbing can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
Dietary Factors: Certain foods, such as those high in sugar or dairy, may contribute to acne by affecting hormone levels and sebum production in some individuals.
Stress: Elevated stress levels can stimulate the production of cortisol, a hormone that may worsen acne by increasing inflammation and oil production.
Genetics: A family history of acne increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
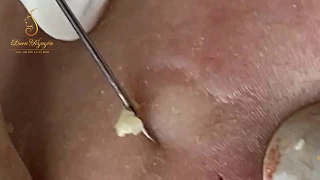
Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, humidity, and the use of makeup or face masks can trap sweat and bacteria, aggravating acne.
Managing facial acne involves maintaining a consistent skincare routine, avoiding known triggers, and consulting a dermatologist for tailored treatments when necessary.
Traditional and Modern Acne Treatment Methods
Traditional Methods:
- Herbal Remedies: Natural ingredients like tea tree oil, aloe vera, turmeric, and neem have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Dietary Adjustments: Traditional wisdom often emphasizes avoiding oily, sugary, or processed foods to maintain clear skin.
- Clay Masks: Bentonite or multani mitti (Fuller’s Earth) helps absorb excess oil and impurities.
- Steam Therapy: Facial steaming opens pores and helps cleanse dirt and oil buildup.
Modern Methods:
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter options like benzoyl peroxide and salicylic acid reduce bacteria and unclog pores. Prescription options include retinoids.
- Oral Medications: Antibiotics, hormonal treatments (e.g., birth control pills), or isotretinoin for severe acne.
- Chemical Peels: Dermatologist-applied acids exfoliate and rejuvenate skin.
- Laser and Light Therapy: Targets bacteria and reduces inflammation for long-term results.
- Extraction and Drainage: For stubborn cysts or nodules, dermatologists perform manual removal.
Combining traditional and modern methods often yields the best results, but consultation with a dermatologist ensures the safest and most effective treatment.